Z=xy^2 New Resources Pythagoras' Theorem Area dissection 2;Curves in R2 Graphs vs Level Sets Graphs (y= f(x)) The graph of f R !R is f(x;y) 2R2 jy= f(x)g Example When we say \the curve y= x2," we really mean \The graph of the function f(x) = x2"That is, we mean the set f(x;y) 2R2 jy= x2g Level Sets (F(x;y) = c) The level set of F R2!R at height cis f(x;y) 2R2 jF(x;y) = cg Example When we say \the curve x 2 y = 1," we really mean \The how can i draw graph of z^2=x^2y^2 on matlab Follow 130 views (last 30 days) Show older comments Rabia Kanwal on Vote 0 ⋮ Vote 0 Commented Walter Roberson on Accepted Answer Star Strider 0 Comments Show Hide 1 older comments Sign in to comment Sign in to answer this question
How To Draw Y 2 X 2
X^2+y^2+z^2=16 graph
X^2+y^2+z^2=16 graph-Example 1 Let f ( x, y) = x 2 − y 2 We will study the level curves c = x 2 − y 2 First, look at the case c = 0 The level curve equation x 2 − y 2 = 0 factors to ( x − y) ( x y) = 0 This equation is satisfied if either y = x or y = − x Both these are equations for lines, so the level curve for cLevel surfaces For a function $w=f(x,\,y,\,z) \, U \,\subseteq\, {\mathbb R}^3 \to {\mathbb R}$ the level surface of value $c$ is the surface $S$ in $U \subseteq



Match Each Function With Its Graph Give Reasons For Chegg Com
The graph z = x2 y2 of the function f(x,y) = x2 y2 which is a paraboloid Note however that most surfaces of the form g(x,y,z) = c can not be written as graphs The sphere is an example, where we need two graphs to cover it Planes ax by cz = d is a plane With ~n = ha,b,ci and ~x = hx,y,zi, we can rewrite theA sphere is the graph of an equation of the form x 2 y 2 z 2 = p 2 for some real number p The radius of the sphere is p (see the figure below) Ellipsoids are the graphs of equations of the form ax 2 by 2 cz 2 = p 2, where a, b, and c are all positiveGraph of z = f(x,y) Discover Resources Shifting and Scaling logarithmic Graphs;
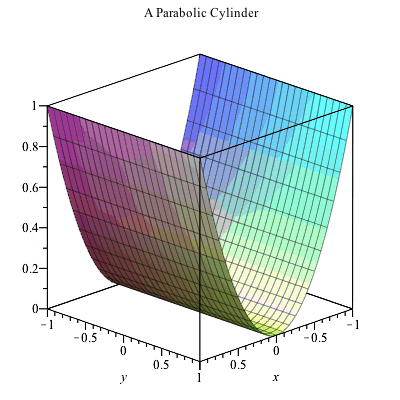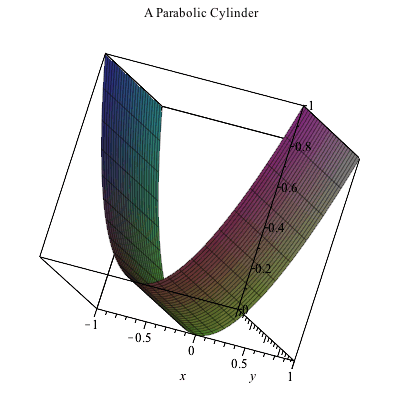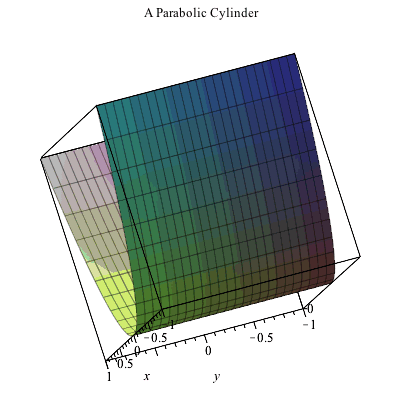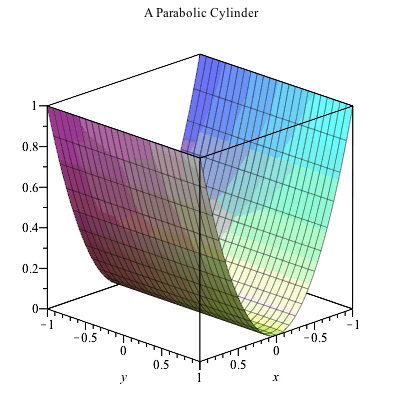
Answer and Explanation The graph of z = x2y2 z = x 2 y 2 is illustrated below As we can see, we can describe the graph of z as a parabolic cylinder directed towards the z axisWhere the two surfaces intersect z = x2 y2 = 8 − x2 − y2 So, 2x2 2y2 = 8 or x2 y2 = 4 = z, this is the curve at the intersection of the two surfaces Therefore, the boundary of projected region R in the x − y plane is given by the circle x2 y2 = 4 So R can be treated as a y simple region in theBut avoid Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers
$\begingroup$ Yep, the first method will be easier for my students to understand, so that is my preference I think I understand what it does so I will be able to explain it to the students It plots the level surface for z, and because of Mesh>Range4, it plots the level surfaces z=1, z=2, z=3, z=4, which are the four planesQuestion X^2 Y^2 Z^2 = 0 In A 3D Graph This problem has been solved!Take the square root of both sides of the equation x^ {2}y^ {2}z=0 Subtract z from both sides y^ {2}x^ {2}z=0 Quadratic equations like this one, with an x^ {2} term but no x term, can still be solved using the quadratic formula, \frac {b±\sqrt {b^ {2}4ac}} {2a}, once they are put in standard form ax^ {2}bxc=0



What Is The Volume Between Paraboloid Z X 2 Y 2 And Y X 2 Z 2 Quora




Part Elliptic Paraboloid Z X2 Y2 Which Editorial Stock Photo Stock Image Shutterstock
A saddle point (in red) on the graph of z=x 2 −y 2 (hyperbolic paraboloid) Saddle point between two hills (the intersection of the figureeight z {\displaystyle z} contour) In mathematics , a saddle point or minimax point 1 is a point on the surface of the graph of a function where the slopes (derivatives) in orthogonal directions are all Since y^2 = x − 2 is a relation (has more than 1 yvalue for each xvalue) and not a function (which has a maximum of 1 yvalue for each xvalue), we need to split it into 2 separate functions and graph them together So the first one will be y 1 = √ (x − 2) and the second one is y 2Then we select to add an Implicit Surface from the Add to graph menu Enter z^2 x^2 y^2 = 2 in the corresponding textbox and select the checkbox (or press enter) to plot it This is the level surface for \(C = 2\text{}\) Print it out, if desired, using the Print Plot option on the app main menu



2




X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Graph Dawonaldson
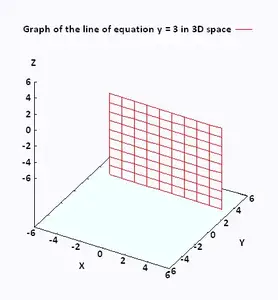
So, in a 3D coordinate system this is a plane that will be parallel to the y z y z plane and pass through the x x axis at x = 3 x = 3 Here is the graph of x = 3 x = 3 in R R Here is the graph of x = 3 x = 3 in R 2 R 2 Finally, here is the graph of x = 3 x = 3 in R 3 R 3Plot z=x^2y^2 WolframAlpha Assuming "plot" is a plotting function Use as referring to geometry instead 3D and Contour Grapher A graph in 3 dimensions is written in general z = f(x, y)That is, the zvalue is found by substituting in both an xvalue and a yvalue The first example we see below is the graph of z = sin(x) sin(y)It's a function of x and y You can use the following applet to explore 3D graphs and even create your own, using variables x and y




X 2 Y 2 Z Graph Novocom Top



Surfacesandcontours Html
(e) Below is the graph of z = x2 y2 On the graph of the surface, sketch the traces that you found in parts (a) and (c) For problems 1213, nd an equation of the trace of the surface in the indicated plane Describe the graph of the trace 12 Surface 8x 2 y z2 = 9;See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Previous question Next question Transcribed Image Text from this Question x^2 y^2 z^2 = 0 in a 3D graph Get more help from CheggGraph the parent quadratic (y = x^2) by creating a table of values using select x values The graph of this parent quadratic is called a parabolaNOTE Any




Graph Of Z 1 X 2 Y 2 Novocom Top




How To Draw Y 2 X 2
Soln The top surface of the solid is z = 4 and the bottom surface is z = x2 y2 over the region D defined in the xyplane by the intersection of the top and bottom surfaces 2 Figure 3 The intersection gives 4 = x2 y2 Therefore D is a disk of radius 2 By the symmetry principle, ¯x = ¯y = 0 We only compute ¯z m = ZZZ E 1dV = ZZ D Z 4Answer to Find the volume of the solid bounded by the paraboloid z = x^2 y^2 and the plane z = 9 in rectangular coordinates By signing up,It's the equation of sphere The general equation of sphere looks like math(xx_0)^2(yy_0)^2(zz_0)^2=a^2/math Wheremath (x_0,y_0,z_0)/math is the centre of the circle and matha /math is the radious of the circle It's graph looks




Find The Area Of The Paraboloid Z 1 X 2 Y 2 That Lies In The First Octant Study Com



Image Graph Of Equation Z X 2 Xy Y 2 Equation
Okay, so we have mathz = x^2 y^2/math describing the paraboloid and we have mathx^2 y^2 = 2y/math describing the cylinder That's how they look like together We want the equation describing the cylinder to be in its conventional formDOWNLOADHD!!F9 Fast and Furious 9 (21) 1080P Full OnlineFsurf (f, 4 4 4 4) Note that this will work if you have access to th Symbolic Math Toolbox If you dont have it, the answer from KSSV will always work Best regards




How To Plot X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Graph Of Z X 2 Y 2 Download Scientific Diagram
Hi, use syms x y f (x,y) = x^2 y^2;The green parabolas open downward, while the purple ones open upward Also, the hyperbolas which make up the horizontal cross sections can open in either the x or y direction, depending on the chosen value for z AllAn ellipsoid is a surface described by an equation of the form x2 a2 y2 b2 z2 c2 = 1 Set x = 0 to see the trace of the ellipsoid in the yz plane To see the traces in the xy and xz planes, set z = 0 and y = 0, respectively Notice that, if a = b, the trace in the xy plane is a circle




Integrating In Cylindrical Coordinates




Graph Of Z X 2 Y 2 Novocom Top
Graph z = x 2 y 2 Graph z = x 2 y 2 Graph z = 2x 2 2y 2 WrapUp At this point, students should be able to classify a paraboloid as "elliptic" or "hyperbolic" based on its shapePlane z = 1 The trace in the z = 1 plane is the ellipse x2 y2 8 = 1 See the explanantion This is the equation of a circle with its centre at the origin Think of the axis as the sides of a triangle with the Hypotenuse being the line from the centre to the point on the circle By using Pythagoras you would end up with the equation given where the 4 is in fact r^2 To obtain the plot points manipulate the equation as below Given" "x^2y^2=r^2" ">"
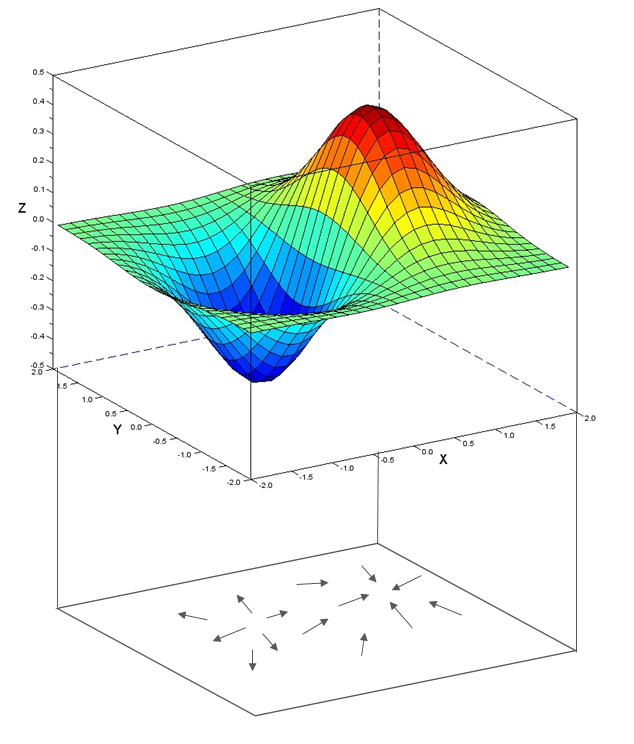



Laplacian And Its Use In Blur Detection By Sagar Medium



1
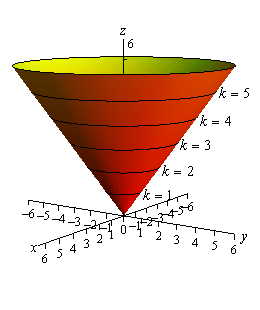
Graphs Solve Equations Surface integrals Find the area of the portion of the cone x^2y^2=z^2 above the xy plane and inside the cylinder x^2y^2=ax Surface integrals Find the area of the portion of the cone x 2 y 2 = z 2 above the x y plane and inside the cylinder x 2 y 2 = a xGraph x^2y^2=4 x2 − y2 = 4 x 2 y 2 = 4 Find the standard form of the hyperbola Tap for more steps Divide each term by 4 4 to make the right side equal to one x 2 4 − y 2 4 = 4 4 x 2 4 y 2 4 = 4 4 Simplify each term in the equation in order to set the right side equal to 1 1 The standard form of an ellipse or hyperbola requiresLook at the picture on the left, which shows the surface z = x 2 y 2 Notice that the parabolas open in different directions;
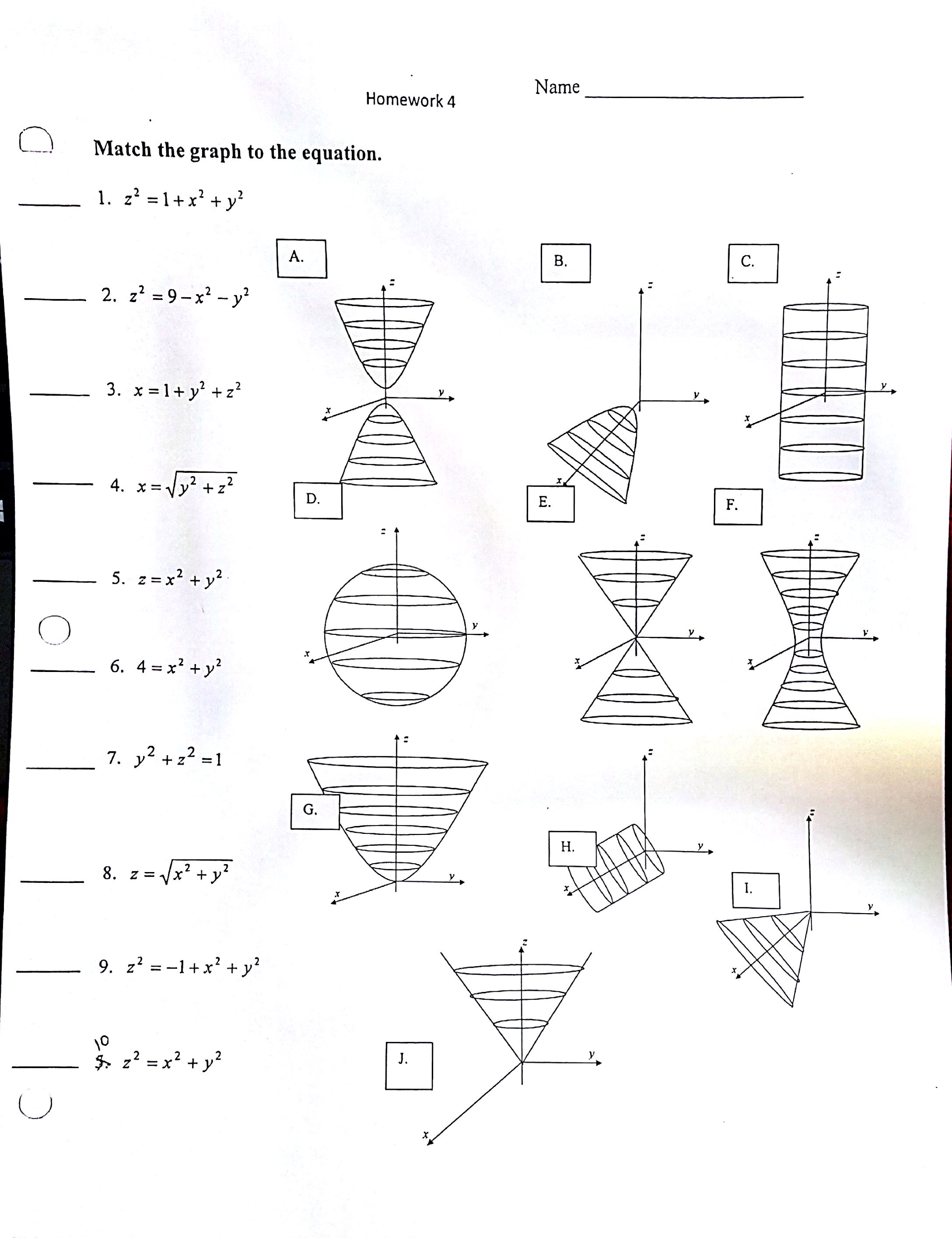



Match The Graph To The Equation X 2 1 X 2 Y 2 Chegg Com



Parameterized Surfaces 2 Html
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge andAmong all the points on the graph of z=10x^{2}y^{2} that lie above the plane x2 y3 z=0, find the point farthest from the plane Boost your resume with certification as an expert in up to 15 unique STEM subjects this summerA function of y, and graph that function in the yzplane Using these graphs as guides, in conjunction with level curves, it is then easier to visualize what the rest of the graph of f looks like Example Let z= x2 y4 Setting y= 0 yields z= x2, the graph of which is a parabola in the xzplane



Solved Graph The Functions F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 F X Y E Sqrt X 2 Y 2 F X Y Ln Sqrt X 2 Y 2 F X Y



Level Surfaces
Thanks for contributing an answer to Mathematics Stack Exchange!Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube For more information and source, see on this link https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=mftj8z8hWQAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



Solved Graph The Functions F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 F X Y E Sqrt X 2 Y 2 F X Y Ln Sqrt X 2 Y 2 F X Y



Homework 3 Model Solution Han
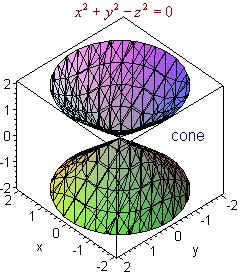
Please be sure to answer the questionProvide details and share your research! z 2 = z ⇒ x 2 – y 2 i2xy = x – iy Therefore, x 2 – y 2 = x (1) and 2xy = – y (2) From (2), we have y = 0 or x = 1/2 When y = 0, from (1), we get x 2 – x = 0, ie, x = 0 or x = 1 When x =1/2, from (1), we get y 2 = 1/4 1/2 or y 2 =3/4, ie, y =±√3/2 Hence, the solutions of the given equation are3 Answers3 Write it as x 2 z 2 = y 2 Note that y is the hypotenuse of a triangle with length x and height z So, this forms a circular cone opening as you increase in y or decrease in y This figure is the (double) cone of equation x 2 = y 2 − z 2 The gray plane is the plane ( x, y) You can see that it is a cone noting that for any y



2




How To Plot X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Sin (x)cos (y)=05 2x−3y=1 cos (x^2)=y (x−3) (x3)=y^2 y=x^2 If you don't include an equals sign, it will assume you mean " =0 " It has not been well tested, so have fun with it, but don't trust it If it gives you problems, let me know Note it may take a few seconds to finish, because it has to do lots of calculations It is the equation of a circle Probably you can recognize it as the equation of a circle with radius r=1 and center at the origin, (0,0) The general equation of the circle of radius r and center at (h,k) is (xh)^2(yk)^2=r^2Surfaces and Contour Plots Part 4 Graphs of Functions of Two Variables The graph of a function z = f(x,y) is also the graph of an equation in three variables and is therefore a surfaceSince each pair (x,y) in the domain determines a unique value of z, the graph of a function must satisfy the "vertical line test" already familiar from singlevariable calculus




Matlab Tutorial




How To Plot X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Z = x 2 y 2 One important feature of the vertical cross sections is that the parabolas all open in the same direction That isn't true for hyperbolic paraboloids!How To Plot X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange For more information and source, see on this link https//mathstackexchangecom/questions//howtoplotGraph x^2y^2=1 x2 − y2 = −1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Find the standard form of the hyperbola Tap for more steps Flip the sign on each term of the equation so the term on the right side is positive − x 2 y 2 = 1 x 2 y 2 = 1 Simplify each term in the equation in order to set the right side equal to 1 1 The standard form of an




13 1 Functions Of Multiple Variables Mathematics Libretexts




Multi Variable Functions Surfaces And Contours Calculus Tutorials
Sketch a graph of the paraboloid z = x^2 y^2 Determine whether the outward normal vector N should point in the k or k direction, and calculate N in terms of x and y Give equations for the tangent plane and normal line at the point P_0 = (2, 2, 8) Find the point where the normal line crosses the xyplaneNote that in this case, the horizontal cross sections are actually circles, but this isn't always the caseThe graph of a 3variable equation which can be written in the form F(x,y,z) = 0 or sometimes z = f(x,y) (if you can solve for z) is a surface in 3D One technique for graphing them is to graph crosssections (intersections of the surface with wellchosen planes) and/or traces




Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube



Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra
This tool graphs z = f (x,y) mathematical functions in 3D It is more of a tour than a tool All functions can be set different boundaries for x, y, and z, to maximize your viewing enjoyment This tool looks really great with a very high detail level, but you may find it more comfortable to use less detail if you want to spin the model



How Do You Graph Z Y 2




Traces Of The Level Surface Z 4x 2 Y 2 Mathematica Stack Exchange



Gnuplot Demo Script Singulr Dem
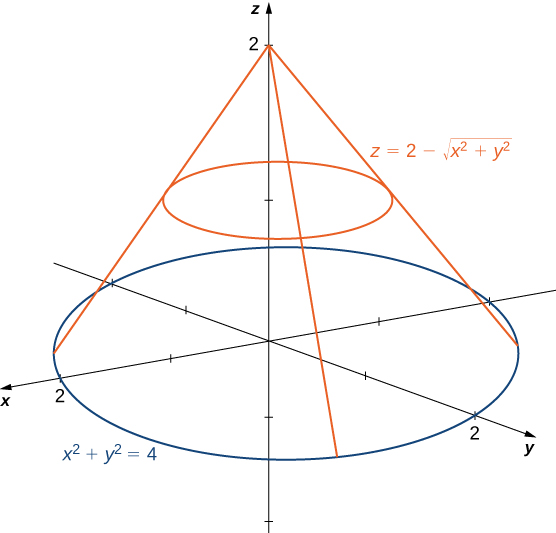



Double Integrals In Polar Coordinates Calculus Volume 3



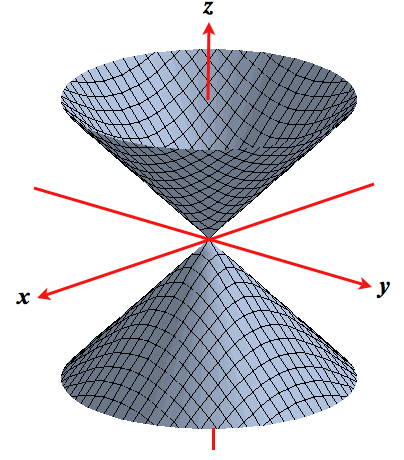
Hyperboloids And Cones
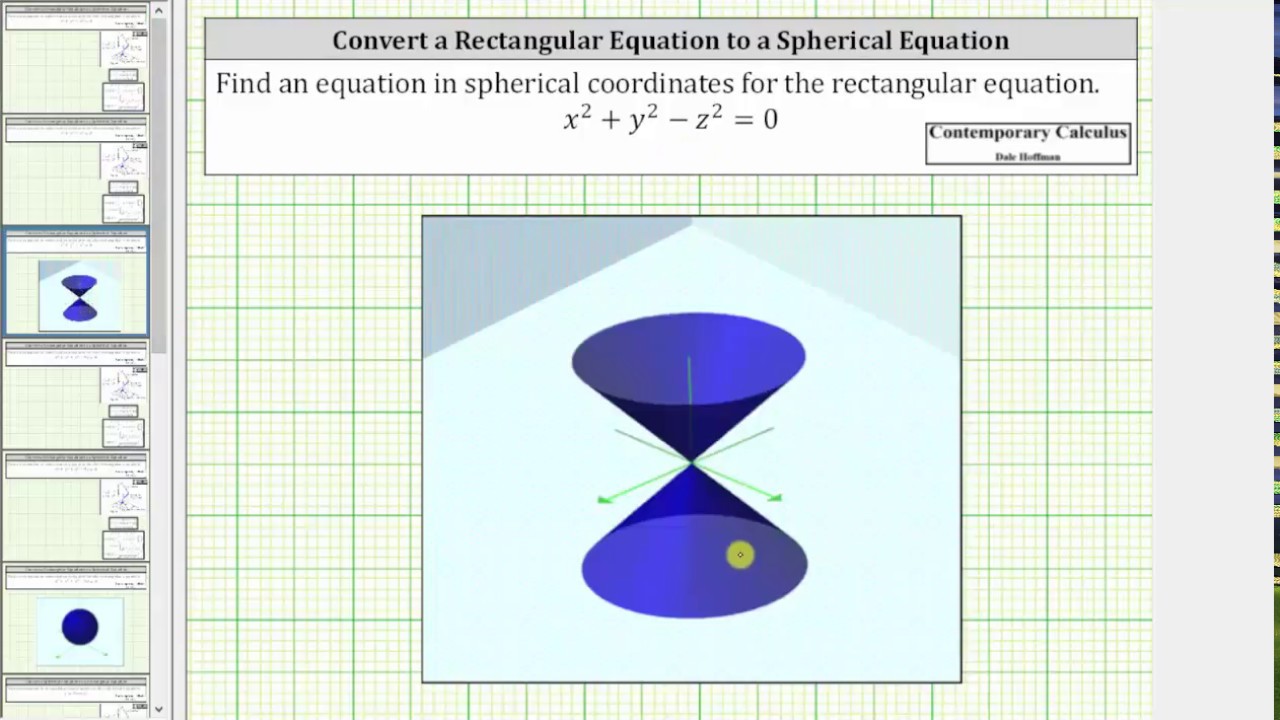



Convert A Rectangular Equation To A Spherical Equation X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Youtube




Draw The Graph Of The Surface Given By Z 1 2 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Study Com




Graph The Triangle With Vertices X 3 2 Y 2 3 And Z 1 1 And Its Image After A Dilation With Brainly Com
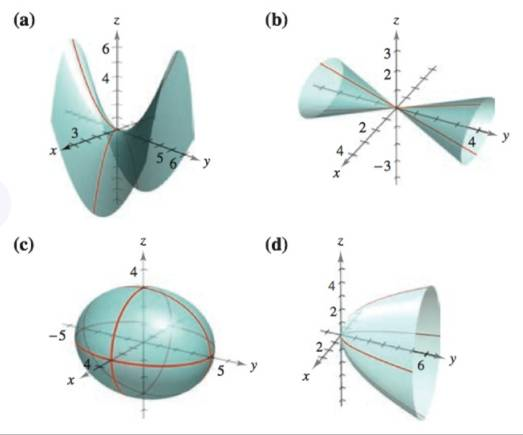



Matching In Exercises 5 10 Match The Equation With Its Graph The Graphs Are Labeled A B C D E And F X 2 9 Y 2 16 Z 2 9 1 Bartleby
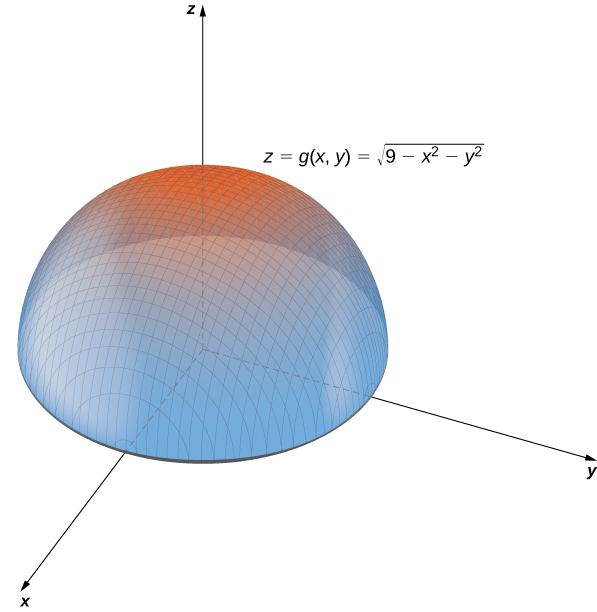



Graphing Functions Of Two Variables By Openstax Jobilize
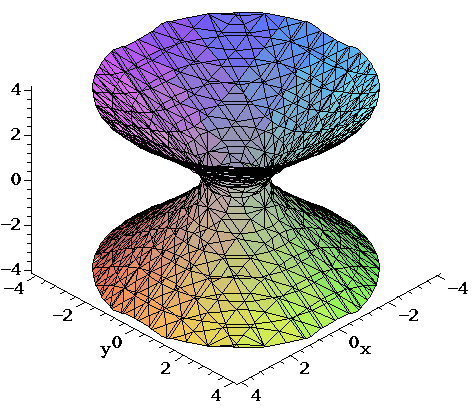



Surfaces Part 2



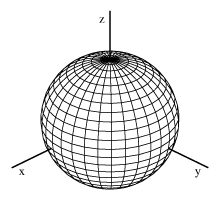
What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora



Plotting In 3d




Cylindrical Coordinates In Matlab




Graphs Of 2 Variable Functions



Gnuplot Demo Script Singulr Dem



Section 15 2 A Brief Catalogue Of The Quadratic Surfaces Projections Ppt Video Online Download




Saddle Point Wikipedia



2
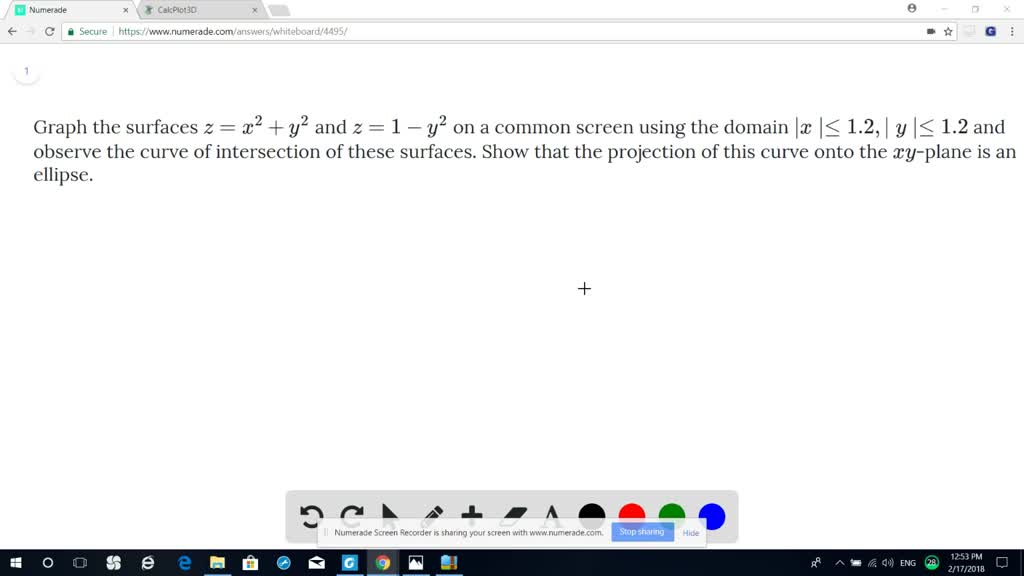



Solved Graph The Surfaces Z X 2 Y 2 And Z 1



Level Surfaces



How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic



Pbaspect Matlab Functions
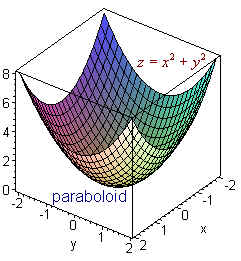



Surfaces




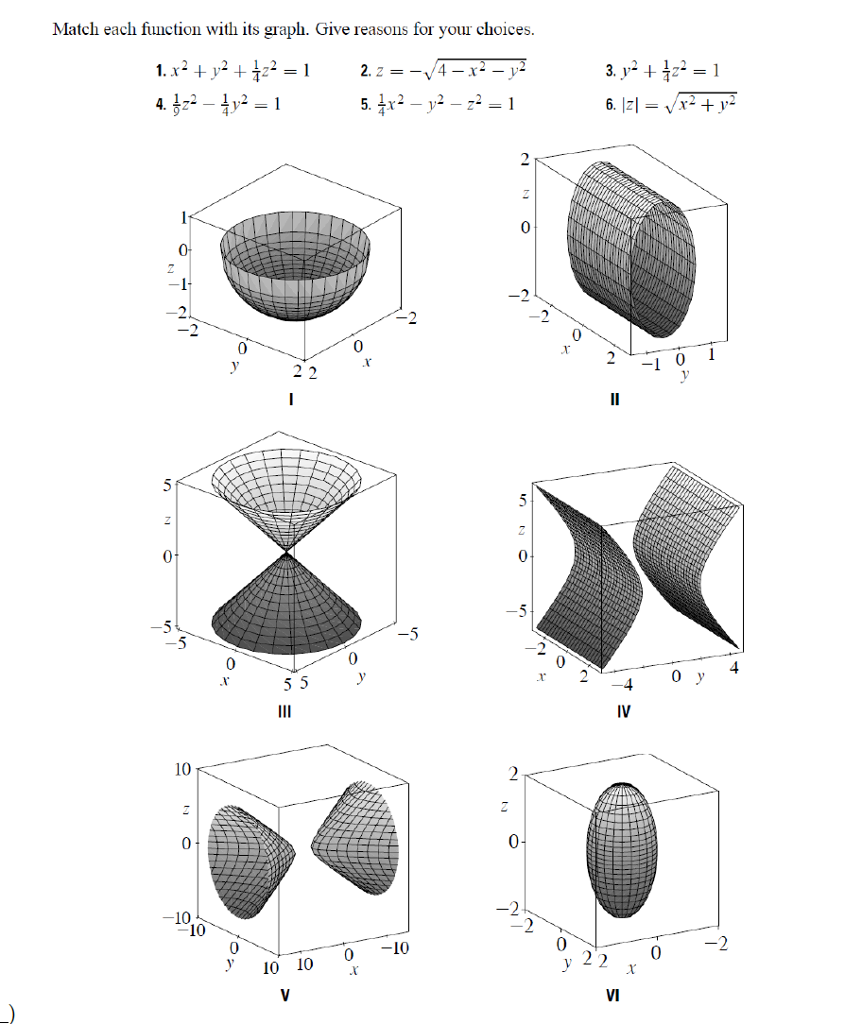
Match Each Function With Its Graph Give Reasons For Chegg Com




The Graph Of The Equation X 2 Y 2 0 In The Three Dimensional Spa



2



Y 2 Z 2 16 Is This Represents A Circle In 3 Dimensional Space Or 2 Dimensional Space Socratic
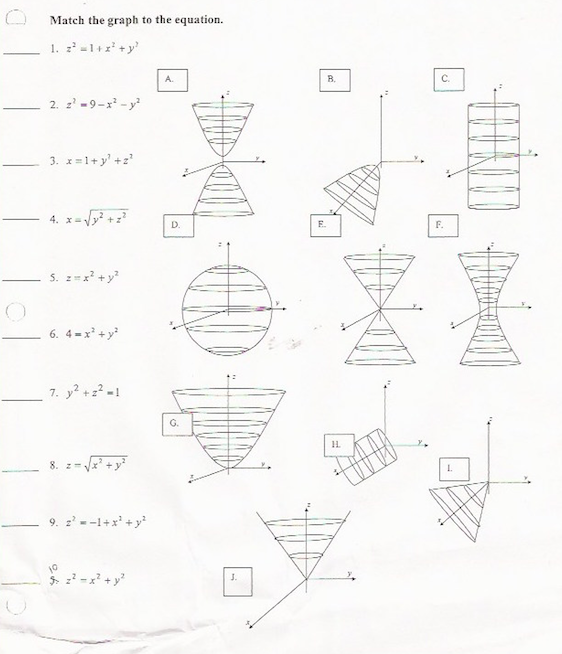



Match The Graph Equation Z 2 1 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Chegg Com
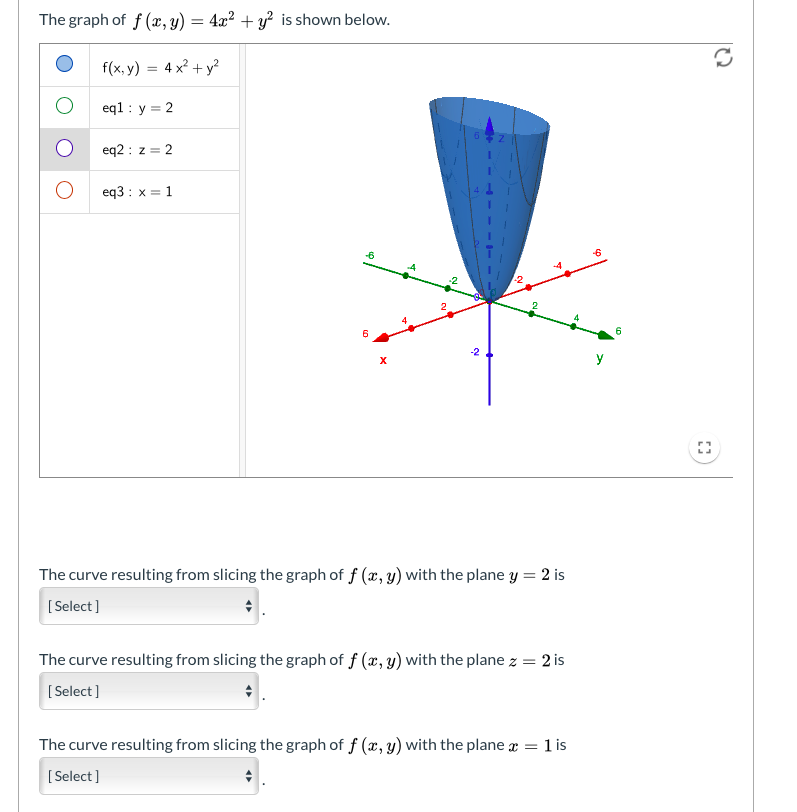



The Graph Of F X Y 4 X2 Y2 Is Shown Below Chegg Com
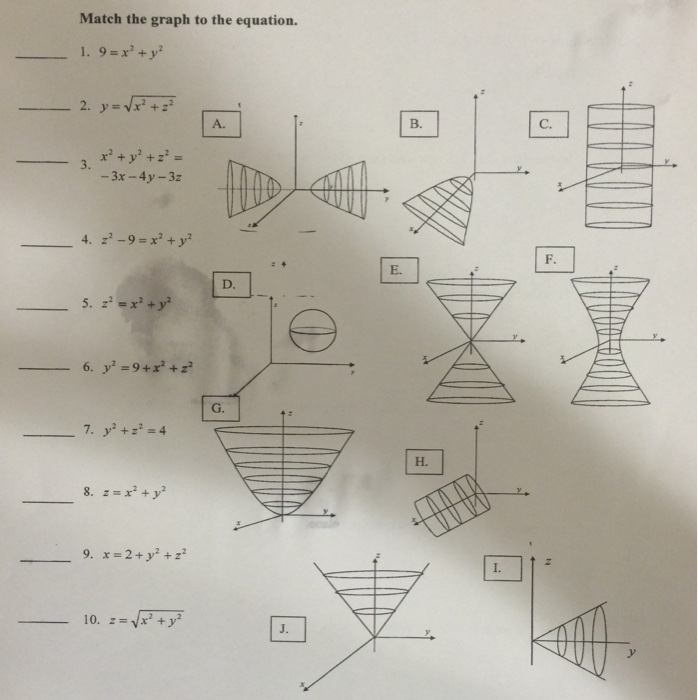



Match The Graph To The Equation 9 X 2 Y 2 Y Chegg Com



Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits




13 Cool Graphs Ideas Graphing Parametric Equation Engineering Humor




Draw The Solid Bounded By The Paraboloid Z 6 X 2 Y 2 And The Plane Z 0 Study Com



Surface Area




Plot A Graph Of The Equation Y 2 X 2 2z 2 Study Com




Consider Z Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Give The Domain And Range Draw The Zx And Zy Traces In Two Homeworklib




What Is The Domain Of F X Y E Sqrt X 2 Y 2 And How Do You Sketch It Quora



3d Surface Plotter Academo Org Free Interactive Education



Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables




Se11f01 01 Gif



Practice Final Please Work Out Each Of The Problems Below Credit Will Be Based On The Steps Towards The Final Answer Show Your Work Problem 1 Sketch The Following A The Point 3 4 1 Solution We Draw The Xyz Axes The Shadow At The Point 3 4 In The



1



No Title




Matlab Surfaces Of Revolution Trigonometric Functions Sine



Mathematics Calculus Iii



Surfaces Part 2



Quadricsurfaces Html




Answered 1 2 3 4 5 6 Match The Function To Bartleby



Search Q Ellipsoid Tbm Isch



Surfaces
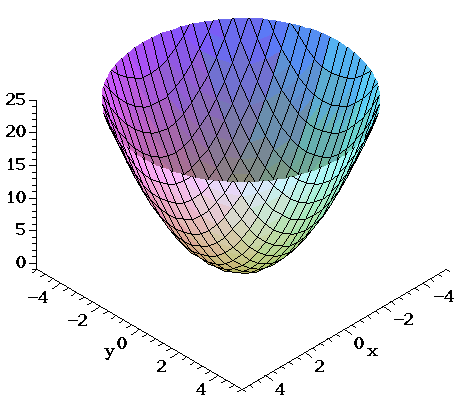



Surfaces Part 2




9 Vectors And The Geometry Of Space Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer 9 6 Functions And Surfaces Functions Of Two Variables 3



The Complex Squaring Function In Polar Coordinates




If X X 1 X 2 Represents



Polar Html




1 What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 23 What Are Its Lines Of Symmetry What Are The Domain And Range Brainly In
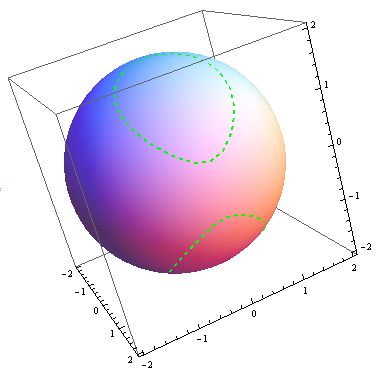



Plotting 3d Surface Intersections As 3d Curves Online Technical Discussion Groups Wolfram Community




Contour Cut Of A 3d Graph In Matlab Stack Overflow
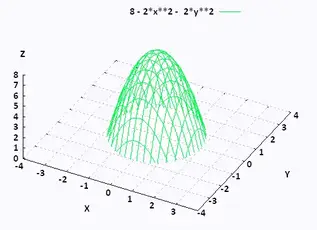



Mathematics Calculus Iii




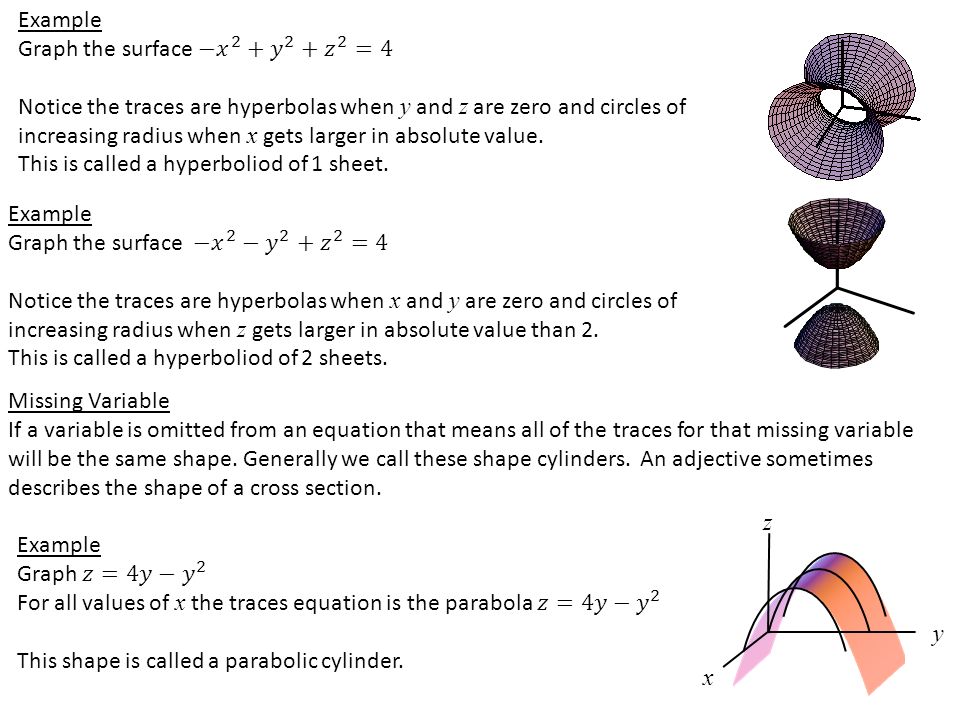
Cylinders And Quadratic Surfaces A Cylinder Is The Continuation Of A 2 D Curve Into 3 D No Longer Just A Soda Can Ex Sketch The Surface Z X Ppt Download



Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables And Surfaces



28 Match The Equation Y X 2 Z 2 With Its Graph Labeled I Viii Toughstem
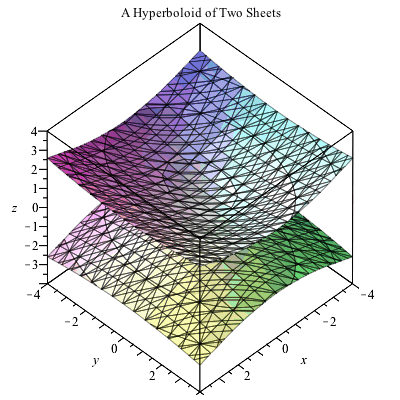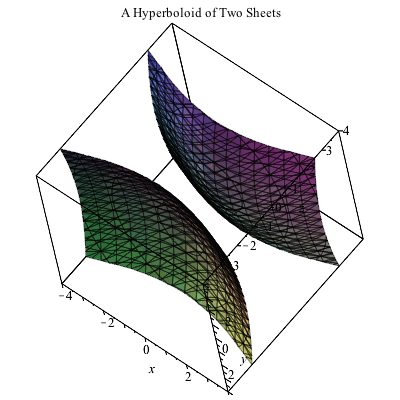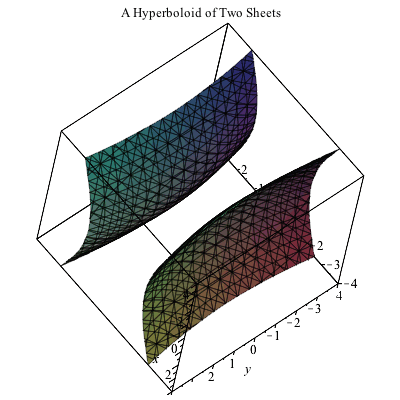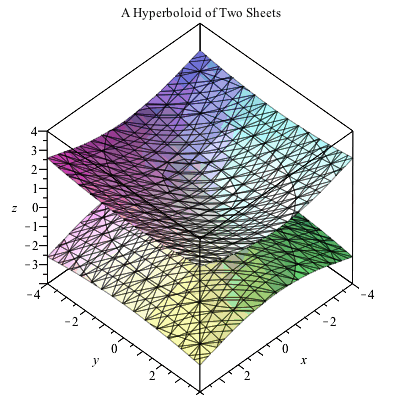



Plotting In 3d



2



Equation Of A Sphere Graph Physics Forums



1




Graphs And Level Curves
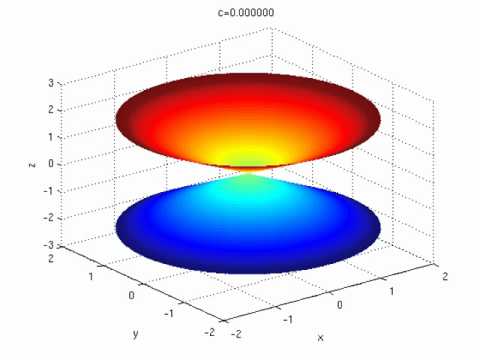



X 2 Y 2 Z 2 C Youtube




6 7 Maxima Minima Problems Mathematics Libretexts




Graphs Of A Z X 2 Y 2 B Z X 2 Y 2 C Z E 2 X 2 Y Download Scientific Diagram




How To Fill A Solid Defined By X 2 Y 2 9 Z 16 X 2 Y 2 And Z 0 Using Pgfplots Tex Latex Stack Exchange



Surfaces Part 2




Drawing Cylinders In Matlab



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿